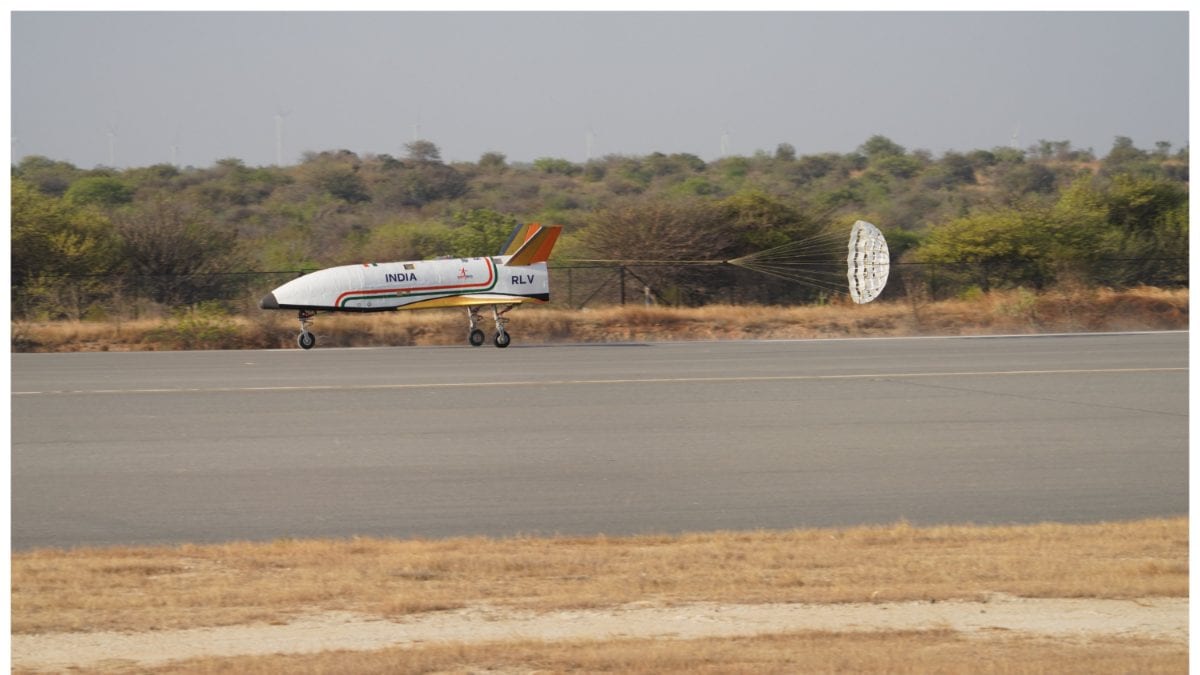
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on Sunday efficiently performed the Reusable Launch Vehicle Autonomous Landing Mission (RLV LEX).
The take a look at was performed on the Aeronautical Test Range (ATR) in Chitradurga, Karnataka, the nationwide area company stated. ISRO performed the experiment in collaboration with the Air Force and Defence Space Research Organisation.
ISRO took to Twitter over the profitable conduct of the touchdown mission and stated “India achieved it!”
“India achieved it! ISRO, joined by @DRDO_India @IAF_MCC, successfully conducted the Reusable Launch Vehicle Autonomous Landing Mission (RLV LEX) at the Aeronautical Test Range (ATR), Chitradurga, Karnataka in the early hours on April 2, 2023,” the tweet learn.
India 🇮🇳 achieved it!ISRO, joined by @DRDO_India @IAF_MCC, efficiently performed the Reusable Launch Vehicle Autonomous Landing Mission (RLV LEX)
on the Aeronautical Test Range (ATR), Chitradurga, Karnataka within the early hours on April 2, 2023.
— ISRO (@isro) April 2, 2023
ISRO efficiently performed the Reusable Launch Vehicle Autonomous Landing Mission (RLV LEX). The take a look at was performed on the Aeronautical Test Range (ATR), Chitradurga, Karnataka within the early hours on April 2, 2023.
According to a ISRO press launch, the RLV took off at 7:10 am by a Chinook Helicopter of the Indian Air Force as an ‘underslung load” and flew to a height of 4.5 km (above MSL).
“Once the predetermined pillbox parameters were attained, based on the RLV’s Mission Management Computer command, the RLV was launched in mid-air, at a down vary of 4.6 km,” the press launch stated.
“Release circumstances included 10 parameters masking place, velocity, altitude and physique charges, and so forth. The launch of RLV was autonomous. RLV then carried out method and touchdown maneuvers utilizing the Integrated Navigation, Guidance & management system and accomplished an autonomous touchdown on the ATR air strip at 7:40 AM IST. With that, ISRO efficiently achieved the autonomous touchdown of an area automobile,” it added.
‘State-of-the-art Technologies’
The autonomous landing was carried out under the exact conditions of a Space Re-entry vehicle’s landing —high speed, unmanned, precise landing from the same return path— as if the vehicle arrives from space, ISRO said.
“Landing parameters such as Ground relative velocity, the sink rate of Landing Gears, and precise body rates, as might be experienced by an orbital re-entry space vehicle in its return path, were achieved,” ISRO stated.
The area company stated that RLV LEX demanded a number of “state-of-the-art applied sciences” including accurate navigation hardware and software, Pseudolite system, ‘Ka-band’ Radar Altimeter, ‘NavIC’ receiver, indigenous landing gear, Aerofoil honey-comb fins and brake parachute system.
A First In The World
In a first in the world, ISRO said, a winged body has been carried to an altitude of 4.5 km by a helicopter and released for carrying out an autonomous landing on a runway.
According to ISRO, RLV is essentially a “space plane with a low lift to drag ratio requiring an approach at high glide angles that necessitated a landing at high velocities of 350 kmph”.
The touchdown experiment utilised a number of indigenous methods, ISRO stated, addign that localised navigation methods primarily based on pseudolite methods, instrumentation, and sensor methods, and so forth., have been developed by it.
“Digital Elevation Model (DEM) of the touchdown web site with a Ka-band Radar Altimeter supplied correct altitude info. Extensive wind tunnel exams and CFD simulations enabled aerodynamic characterization of RLV previous to the flight. Adaptation of latest applied sciences developed for RLV LEX turns different operational launch autos of ISRO less expensive,” ISRO stated.
Read all of the Latest Tech News right here
Source web site: www.news18.com