The challenge of world debt misery is a matter of nice concern, not only for the affected creating nations but in addition for developed international locations and worldwide organizations. A current United Nations Development Program report revealed that 54 creating economies are at the moment grappling with extreme debt issues. Among these nations, Ghana, Zambia, and Sri Lanka have discovered themselves in dire monetary straits. Sri Lanka’s authorities declared chapter in April 2022, briefly suspending exterior debt repayments till a consensual restructuring plan aligned with the International Monetary Fund’s financial adjustment program may very well be established. Ghana defaulted in December 2022, whereas Zambia confronted monetary problem in repaying loans again in June 2020.
Common Challenges in Ghana, Zambia, and Sri Lanka
The debt crises in Ghana, Sri Lanka, and Zambia share a standard theme of coverage mismanagement that has given rise to structural imbalances of their respective economies. While every of those international locations confronted distinctive challenges – Sri Lanka with extreme cash printing and disruptive agricultural insurance policies, Ghana with impractical election guarantees, and Zambia with allowances for particular employment and local weather vulnerabilities – the underlying issues weren’t distinctive to those instances. These nations have grappled with inadequately structured tax techniques, the middle-income entice, and the challenges of restructuring bilateral debt with China. The following desk summarizes the explanations for debt crises within the three international locations.
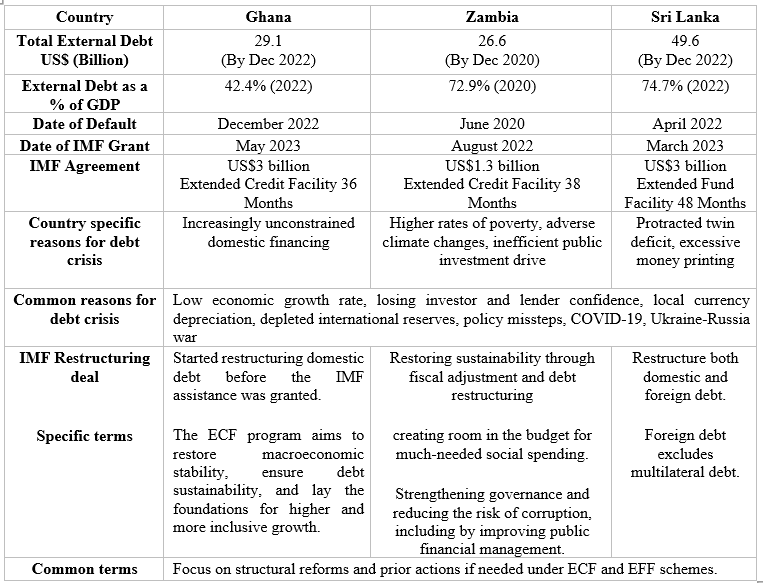
Source: International Monetary Fund (2023), Central Bank Annual Report (2022), External Resource Department of Sri Lanka (2023)
In Sri Lanka, coverage lapses and financial mismanagement led to a multifaceted catastrophe. Ill-timed tax reductions, rushed makes an attempt to undertake natural agriculture, depletion of official reserves whereas striving to keep up a flawless debt servicing file, delayed change price changes, and a failure to take heed to early warning alerts contributed to an financial disaster. As international change reserves dwindled and financial development charges declined, investor confidence plummeted.
Misappropriation of funds and impractical election guarantees within the type of tax cuts and subsidies in Ghana additionally speeded its financial downfall. The main tax reforms included the abolishment of VAT/NHIL on actual property, monetary providers, and import duties in addition to tax reductions on the nationwide electrification scheme levy, public lighting levy, and particular petroleum tax price.
In Zambia, whereas the state of affairs was barely totally different, fiscal imbalances additionally created extra debt pressures. Zambia reinstated allowances for chosen employment-related advantages and confronted financial shocks as a consequence of local weather vulnerabilities, which positioned rising strain on the home economic system.
The three international locations confronted the identical penalties: servicing exterior debt obligations in foreign currency turned more and more troublesome, forcing these nations to depend on non-public credit score markets to acquire international change for debt servicing and important imports. That in the end compounded their debt issues, resulting in sovereign defaults.
IMF Financial Assistance
All three international locations consulted the International Monetary Fund (IMF) as a final resort to deal with their debt crises, and the IMF confirmed willingness to supply help underneath sure circumstances. Due to their lower-middle-income standing, Ghana and Sri Lanka had been handled in a different way from Zambia, a low-income nation. Ghana and Sri Lanka needed to comply with restructure their home debt earlier than receiving monetary help, whereas Zambia had the chance to disregard home debt restructuring.
Ghana obtained a $3 billion Extended Credit Facility (ECF), Sri Lanka a $3 billion Extended Fund Facility (EFF), and Zambia a $1.3 billion ECF. Zambia stood out as the one nation among the many three to profit from the Highly Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) initiative, which enabled the restructuring of money owed with senior collectors such because the World Bank and Asian Development Bank. This safeguarded Zambia’s improvement targets from being compromised by unsustainable debt and gave entry to extra strong types of debt reduction.
This stark distinction marks the “middle-income trap” as a part of the continued international debt disaster. The debt-distressed international locations requiring extra concessional financing are predominantly of middle-income standing, highlighting the necessity for higher mechanisms to handle debt misery past the normal measures.
The Role of China in Debt Restructuring Negotiations
China performs a pivotal position within the international dialog on the debt disaster, as proven within the three creating nations thought of right here. China accounted for round 17.6 p.c of Zambia’s exterior debt. In Ghana, solely 3 p.c of exterior debt is owed to China; nonetheless, this debt is collateralized in opposition to pure sources equivalent to cocoa, bauxite, and oil. China is Sri Lanka’s largest bilateral creditor, to whom Sri Lanka owes round 45 p.c of its bilateral debt. Because China is such a significant bilateral creditor and faces its personal home debt pressures, this created extra challenges when restructuring debt as a part of Sri Lanka’s IMF settlement.
Debt servicing funds comprise a major supply of China’s authorities income as a consequence of its standing as a significant international bilateral creditor by the Belt and Road Initiative. Hence, China is cautious to not set a precedent for beneficiant and simple debt restructuring, as this will likely open the door to serial defaults on bilateral money owed, additional exacerbating financial pressures. Considering these points, as a strategic creditor with much less urge for food for losses, China usually prefers prolonged extensions on debt repayments and resists any reductions within the excellent principal.
This was the expertise of Zambia. In its eventual take care of the Export-Import Bank (Exim) of China, either side agreed to scale back the coupon on its $4 billion in acknowledged official claims to 1 p.c for the rest of Zambia’s IMF program. The settlement with China will see Zambia pay rates of interest as little as 1 p.c till 2037 and push out maturities on $6.3 billion in bilateral debt to 2043, representing a mean extension of greater than 12 years.
As for Sri Lanka, after President Ranil Wickremesinghe’s go to to China in mid-October, Sri Lanka confirmed that it has reached a take care of China, concerning $4.2 billion of debt. This is a optimistic signal for receipt of the second IMF tranche. State Minister for Finance Shehan Semasinghe mentioned the settlement reached with the IMF and the staff-level settlement reached following the primary evaluate of Sri Lanka’s EFF association will assist settle arrears owed to multilateral collectors whereas expediting the debt restructuring course of.
This might give reassurances to Ghana, which is but to finalize a debt restructuring take care of China, because it goals for a versatile and cordial response from collectors with the help of the IMF. However, the difficulties confronted by Ghana, Zambia, and Sri Lanka when restructuring their bilateral debt with China might chase away different potential defaults within the creating world.
Lessons Learned
Developing international locations that default earlier than initiating the debt restructuring course of present comparatively increased losses for traders. The experiences of Ghana, Zambia, and Sri Lanka counsel that reaching out to the IMF earlier than a default is essential to stopping rejection by potential lenders.
This state of affairs ought to function a wake-up name for the World Bank, IMF, and different multilateral organizations to evolve mechanisms that handle this unprecedented debt disaster and promote higher initiatives for financial improvement. Without efficient debt restructuring, reduction, or forgiveness, middle-income debtor nations threat falling right into a debt entice the place financial insurance policies focus solely on servicing unproductive debt repayments to collectors and propping up an unfair international monetary system.
Many creating economies labeled as middle-income international locations are disadvantaged of concessional financing alternatives and extra beneficiant debt reduction mechanisms, such because the HIPC, offered by worldwide organizations. This should sign to multilateral organizations that mechanisms should evolve to help debt-distressed middle-income international locations, who at the moment dominate international debt misery. Multilateral organizations should help these economies individually to scale back their debt ranges, moderately than holding them again because of arbitrary earnings categorization and a “one-size-fits-all” method.
Prolonged debt restructuring processes as a consequence of delays from main collectors have elevated debt burdens over time. Timely discussions are important for safeguarding a debt-ridden nation’s monetary stability and mitigating potential financial repercussions from extended debt restructuring. The challenges related to IMF insurance policies necessitate entry to various sources of concessional finance to handle the chance prices of debt. It is crucial to navigate these turbulent waters and be sure that nations will not be held hostage by debt however moderately empowered to construct a brighter financial future.
This article is predicated on an explainer titled: “Borrowing Wisely: Gaining Insights from Debt Restructuring in Ghana, Sri Lanka and Zambia” revealed by Lakshman Kadirgamar Institute of International Relations and Strategic Studies.
Source web site: thediplomat.com








