The challenges of mounting debt and local weather change have emerged as two of probably the most urgent points for creating international locations, and Sri Lanka isn’t any exception. The world economic system at present faces critical debt misery, and creating international locations are pressed to seek out modern options that tackle each local weather and debt crises below the constraints of the present world monetary structure.
At the 2023 Summit for a New Global Financing Pact, Sri Lanka’s President Ranil Wickremesinghe known as for a “separate, innovative process for middle-income countries” to handle their debt challenges, and advocated for “timely and automatic access to concessional financing.” In addition, Wickremesinghe known as for multilateral improvement banks and worldwide monetary establishments to find higher options for offering emergency financing for international locations in debt misery, including that macroeconomic reform is important.
During the World Economic Forum’s Annual Meeting of the New Champions, Sri Lankan Foreign Minister Ali Sabry emphasised the significance of sustainable debt restructuring, significantly for creating international locations. Sabry defined that “because of the financial crisis, you can’t put your funding into other important areas such as education, climate change, and renewable energy because you are grappling with your interest and debt payments.”
Sri Lanka’s president and overseas minister have reaffirmed that converging debt and local weather vulnerabilities demand new options and stay two of their authorities’s prime priorities. However, Sri Lanka should discover modern approaches to sustainable improvement, for which entry to local weather finance from developed international locations is important to offset climate-induced inequality.
Climate Debt: The Mismatch Between Climate Change Contribution and Vulnerability
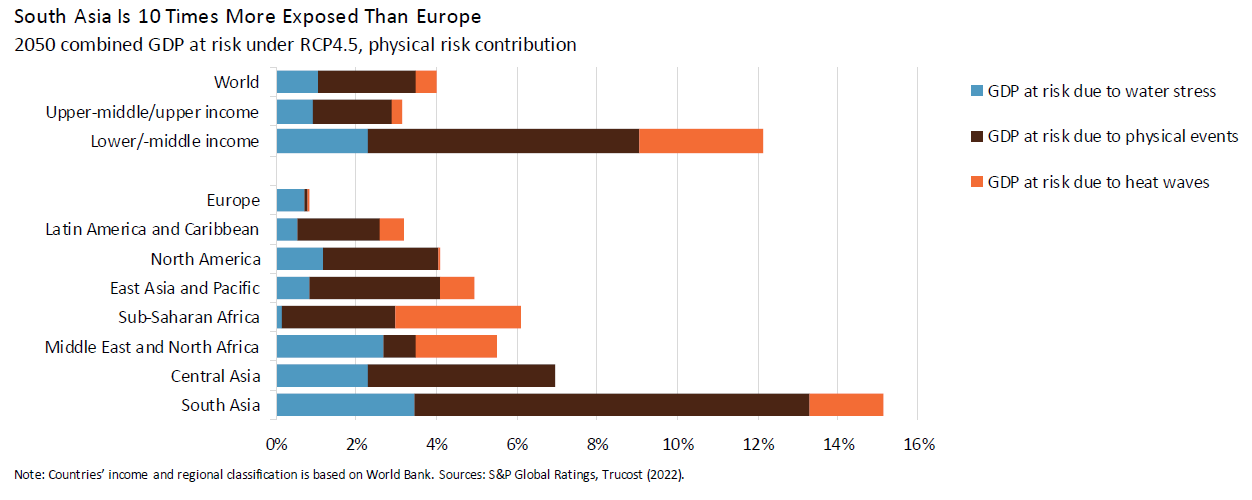
Climate change disproportionately impacts the economies of creating international locations, with 15 % of South Asia’s GDP anticipated to be in danger by 2050. Despite being accountable for solely 21 % of cumulative world carbon emissions, creating international locations stand to lose considerably extra in climate-compromised GDP. Figures 1 and a pair of spotlight this asymmetry:
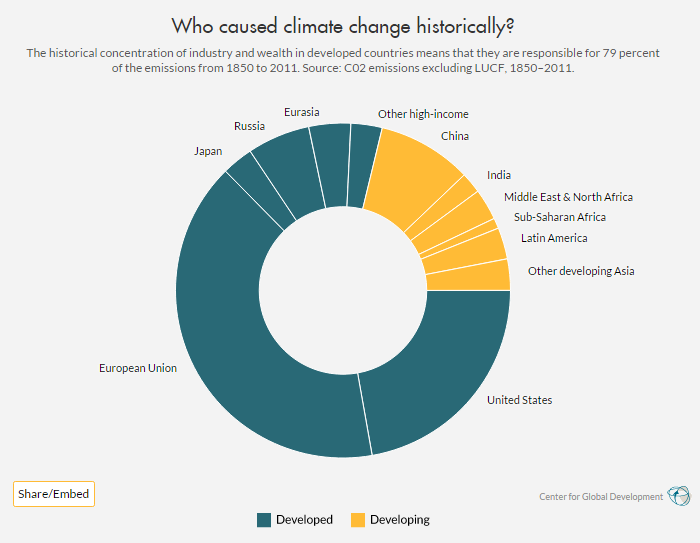
Figure 1: The Contribution of Developed and Developing Countries to CO2 Emissions. Graphic by the Center for Global Development.
Sri Lanka is categorized as “other developing Asia” in Figure 1 and as “South Asia” and “Lower/Middle Income” in Figure 2. These present that Sri Lanka faces disproportionately excessive financial penalties of local weather change relative to its historic contribution, accounting for less than 0.03 % of world cumulative emissions.
Sri Lanka ranks 116th out of 182 international locations on the local weather vulnerability index, with the World Bank projecting that over 90 % of Sri Lanka’s inhabitants at present lives in attainable future hotspots for droughts and floods.
In response to local weather vulnerabilities, Sri Lanka established formidable Nationally Determined Contributions, which embrace commitments to cut back nationwide greenhouse fuel emissions by 14.5 % and produce 70 % of electrical energy via renewable sources by 2030. However, these local weather targets are unlikely to be met resulting from restricted fiscal sources, low tax revenues, and excessive ranges of debt misery.
Sri Lanka requires monetary assist from worldwide collectors to make sure it may possibly mobilize the important funds for climate-resilient investments and adaptation methods, which is able to insulate Sri Lankans from the adverse penalties of local weather change.
Financing Climate Action
Leading economists and coverage specialists have known as for the reform of the worldwide monetary structure, proposing direct actions that developed international locations should take to alleviate debt and local weather burdens on creating international locations. They contend that local weather finance devices are important for creating international locations to handle local weather vulnerabilities within the face of mounting debt pressures, and developed international locations should make this finance accessible via revenue-generating options. Funds for local weather finance devices and local weather reparations should be made obtainable via important reforms to the worldwide monetary structure, the fossil gas business, and world taxation mechanisms so as to redistribute wealth to fund important climate-resilient investments in creating international locations.
1. Reforming the Global Financial Architecture
Climate and debt vulnerabilities are inherently linked via a vicious cycle of debt and local weather crises. Developing international locations with excessive ranges of debt are unable to mitigate local weather danger, leaving them extra susceptible to the implications of local weather change. This “climate-debt trap” drains an estimated $2 trillion per 12 months in sources from low-income international locations. Since 2020, overseas debt repayments have risen by 45 %, inserting Sri Lanka and over half of all low-income international locations in debt misery or excessive danger of debt misery.
Experts argue that the worldwide monetary system is structurally ineffective at addressing world debt crises. Enhancing monetary solidarity between developed and creating economies requires the institution of a brand new multilateral mechanism for sovereign debt forgiveness and cancellation. This ought to contain higher entry to concessional finance for creating international locations complemented by coverage autonomy, relatively than imposing conditionalities and prolonging debt reimbursement intervals.
Governments should have entry to finance that facilitates a long-term perspective to infrastructure funding with non-revenue-generating advantages, which is able to cut back the debt pressures on creating international locations investing in local weather change mitigation. Policies to advertise local weather finance should create new alternatives for a extra sustainable debt surroundings, with out undermining world campaigns for debt justice.
2. Ending Subsidies within the Fossil Fuel Industry
Experts have urged governments to cease funding the fossil gas business and redirect this cash towards local weather finance tasks for creating international locations. On common, G-20 governments present $584 billion yearly as fossil gas handouts, corresponding to via value assist, public finance, and investments into state owned enterprises.
Experts advocate that the G-20 governments finish fossil gas handouts instantly and reallocate this funding to a “Loss and Damage Fund,” which is about to be activated on the twenty eighth session of the Conference of Parties (COP28) in December 2023. Through this fund, wealthy industrialized international locations, whose financial progress was traditionally pushed by fossil fuel-led industrialization, will present monetary help to less-industrialized international locations which are disproportionately extra susceptible to the impacts of local weather change relative to their industrial contribution. Developing international locations’ future progress is inhibited by local weather challenges, so these reparations goal to compensate for this lack of financial potential.
3. Reforming Global Taxation Mechanisms
For the primary time in 25 years, excessive wealth and excessive poverty are rising concurrently. Oxfam reviews that 63 % of all new world capital created within the final two years (amounting to $42 trillion) went to the richest 1 % of society. This enhance in world inequality undermines poverty alleviation efforts but additionally exacerbates local weather inequality.
Economists posit that world wealth taxes are an efficient resolution in redistributing funds and lowering the overdependence on debt for financing improvement tasks in creating international locations. They name for incremental adjustments in excessive wealth taxes starting at 2 %, which might generate substantial funds for improvement and local weather funds.
Moreover, it’s estimated that $483 billion in tax income is misplaced yearly because of tax evasion, 78.3 % of which comes via OECD international locations. One proposed resolution is transferring the accountability of tax regulation from the OECD to the United Nations, which might allow the creation of a common and intergovernmental tax conference.
Furthermore, specialists have known as for governments to make oil and fuel firms pay for the injury that they’ve triggered. It is estimated that the share of emissions of the 21 largest fossil gas firms from 1988-2022 will end in $5.4 trillion in misplaced GDP between 2025 and 2050. This comes at a time when the six heaviest-polluting firms made earnings of over $354 billion in 2022. Economists promote a “polluter pays” tax on fossil gas firms, redirecting $200-300 billion yearly to environmentally sustainable industries that offset fossil fuel-induced local weather damages.
The Way Forward
Experts estimate that implementing the three aforementioned options would unencumber a complete of $3.5 trillion yearly for world local weather motion. Just one-fifth of this determine can be sufficient to finance the loss and injury fund ($400 billion per 12 months), meet the $100 billion per 12 months local weather finance goal, cowl emergency U.N. humanitarian appeals ($52 billion per 12 months), and shut the common power hole ($34 billion per 12 months).
Sri Lanka’s financial and local weather crises display the necessity for concessional finance in debt-distressed economies to handle local weather and debt vulnerabilities concurrently. It is essential that the monetary system explores new options and redirects unproductive capital from debt repayments and subsidies to simpler investments.
This is undoubtedly a troublesome course of and requires vital funding from developed international locations that at present expertise fewer direct penalties from local weather change, however a longer-term technique is required to mitigate future damages. Without entry to concessional local weather finance, creating international locations will proceed to endure disproportionately from the implications of local weather change, which is able to exacerbate future world challenges that can inevitably have an effect on developed international locations.
If Sri Lanka – like different susceptible creating international locations – hopes to fulfill its daring environmental commitments within the face of debt misery, it requires a holistic strategy from collectors and policymakers to reallocate finance to areas with the best financial potential. The authorities should discover local weather finance devices, corresponding to inexperienced bonds, debt-for-nature, and debt-for-climate swaps, alongside ongoing debt restructuring negotiations, as a way of making a extra sustainable debt surroundings and producing vital multiplier results that profit each the economic system and the surroundings.
This article relies on an extended report printed by the Lakshman Kadirgamar Institute of International Relations and Strategic Studies, “Climate Finance: Repairing the Past, Financing the Future.” Access the complete report right here.
Source web site: thediplomat.com