Markets have spent current months girding for a financial coverage pivot to decrease rates of interest by central banks representing roughly a 3rd of the worldwide economic system.
However, regardless of inflation within the U.S., eurozone and the U.Okay. beginning the 12 months nicely down from cycle highs and nearing 2% targets, the European Central Bank on Thursday, at 8:15 a,m. Eastern, would be the first of the excessive profile financial guardians to inform buyers they have to wait a bit longer for rates of interest to fall.
It mustn’t come as a shock.
Derivatives markets are pricing in subsequent to no likelihood that the ECB will trim its deposit price from a file excessive of 4% this week. Similarly, merchants see a 99.5% likelihood that the U.S. Federal Reserve is not going to minimize borrowing prices at its subsequent assembly on January 31. Nor ought to the Bank of England budge the day after that. (Note: the Bank of Japan is predicted to subsequent increase charges).
The subsequent few conferences are a distinct matter. To various levels they’re thought of doubtlessly ‘live’, with price cuts by the Fed, particularly, thought of potential in March, and the market punting on the ECB trimming in June.
Consequently, ECB President Christine Lagarde will likely be first to set the tone for the weeks approaching these potential pivots.
Unfortunately, many analysts suppose it unlikely Lagarde will shift her place on the inflation surroundings she perceives, or give clues throughout her press convention, as to when a price minimize could happen.
“We expect Lagarde to indicate that it is premature to talk about rate cuts. However, she is also likely to stress that ECB decisions are meeting by meeting and are data dependent,” stated Mohit Kumar, Chief European Economist at Jefferies.
Arnaud Marès, chief European economist at Citi, agrees: “[W]e do not expect any meaningful or particularly new communication to come out of this week’s meeting of the Governing Council of the European Central Bank,” he stated.
Indeed, Marès reckons that with eurozone inflation not anticipated to rapidly fall from its present 2.9% — Barclays sees January’s studying dipping barely to 2.7% — an easing of coverage could not come till the summer season.
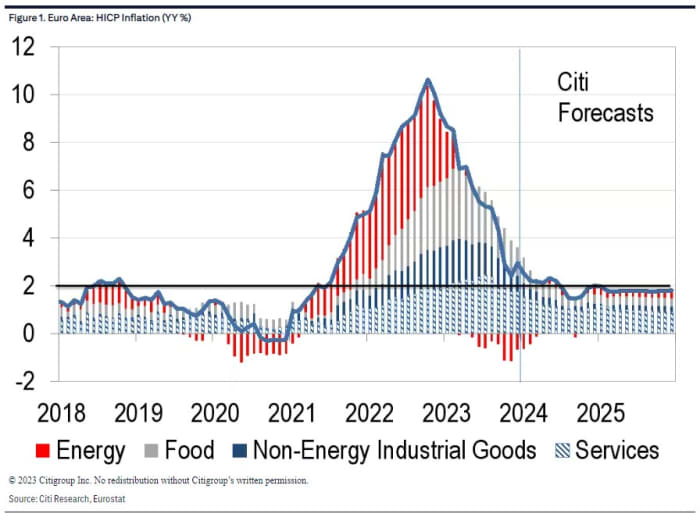
Source: Citi
“So long as the ECB projects 2025 inflation above 2%, we expect resistance to rate cuts to remain strong. Once those projections fall below 2%, we expect pressure to ease policy to become irresistible. We expect this will be the case in June, but not earlier,” stated Marès in a notice to purchasers.
In its newest forecasts, printed final month, the ECB stated it noticed the bloc’s economic system rising 0.8% in 2024 — an acceleration from the anticipated 0.6% enlargement for 2023 — “as real disposable income rises – supported by declining inflation, robust wage growth and resilient employment – and export growth catches up with improvements in foreign demand.”
But this 12 months’s projected progress price is decrease than the 1% forecast in September, and it might be potential the ECB could nudge progress forecasts decrease nonetheless given not too long ago mushy knowledge, akin to weak buying managers’ surveys.
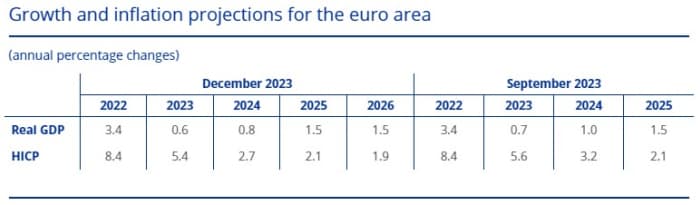
Source: ECB Macroeconomic Projections December 2023
Despite this, feedback from ECB officers of late recommend they’ve been eager, similar to their friends on the Fed, to push again towards merchants’ extra optimistic timing for price cuts.
“We accordingly expect all policy parameters to remain unchanged at the upcoming meeting, and for the formal guidance to reiterate that rates will be set ‘at sufficiently restrictive levels for as long as necessary’,” stated the economics group at Goldman Sachs led by Sven Jari Stehn.
The ECB’s choice to face pat on Thursday, and never suggest a timetable for looser coverage, could also be supported by indications that the impression on financial institution lending of earlier rate-rises is already a lot decreased, in keeping with Nomura.
Analyzing the ECB’s Fourth Quarter 2023 Bank Lending Survey, launched Tuesday, the Nomura group led by George Moran, noticed that the majority the transmission from tighter financial coverage to monetary circumstances has now occurred.
“For some hawks this may be a concern, potentially pushing out when they think rate cuts should happen,” stated Nomura in a notice to purchasers.
“However, we think that the majority of [ECB] Governing Council members are satisfied with the degree of tightening, which has already happened, are pleased that the transmission is slowing down. Hence, we expect cuts from June 2024.”
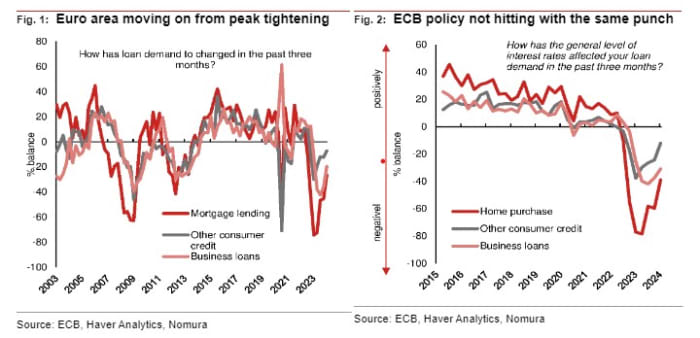
Source: Nomura. Charts from the ECB’s Fourth Quarter 2023 Bank Lending Survey
Goldman’s Stehn, nonetheless thinks decrease charges could come sooner, because the U.S. financial institution sees core inflation falling decrease that the ECB expects, wage progress easing, and the disruption to transport by battle within the Middle East having much less of an impression on inflation than individuals suppose.
“We therefore maintain our modal case for a 25bp cut in April,” stated Goldman. “Waiting until April provides the Governing Council with one more inflation report and some additional color on the Q1 wage negotiations, which we expect to provide enough confidence that inflation is returning to 2% in a sustainable manner.”
The German 2-year bond yield
BX:TMBMKDE-02Y,
the eurozone short-term benchmark, was little modified at 2.719% early Thursday. It has fallen from round 3.3% in October, amid easing inflation and hopes for the ECB pivot.
Source web site: www.marketwatch.com








