The world’s three greatest economies are all going through an enormous downside. We can see it looming over the horizon, nevertheless it’s arduous to totally calculate the impression.
We know the United States, China and Japan are confronting inhabitants challenges. In Japan, the inhabitants has been shrinking since 2010 and China skilled its first inhabitants drop in 60 years in 2022. In the U.S., inhabitants progress is projected to degree off over the approaching years. How can we begin to perceive the financial and market implications of this huge shift?
The dependency ratio is the comparability of a working-aged inhabitants to the younger and aged amongst them. This metric is predictive of the form of the worldwide workforce, measuring which nations are poised to develop economically on the world stage and which of them might undergo economically if actions should not taken to adapt to an growing old inhabitants and decrease delivery charges.
This is vital as a result of, regardless of elevated automation, the number-one driver of financial output is labor. An growing old inhabitants with low fertility charges means the workforce of a inhabitants will decline as retirees cease working and there should not sufficient younger individuals round to exchange them.
The high three nations by GDP (gross home revenue) are the U.S., China and Japan. All three are wrestling with an growing old inhabitants and low delivery charges, which means fewer individuals will probably be coming into the workforce and extra will probably be leaving it by way of retirement or well being causes for not less than the following 25 years.
Demographics are future
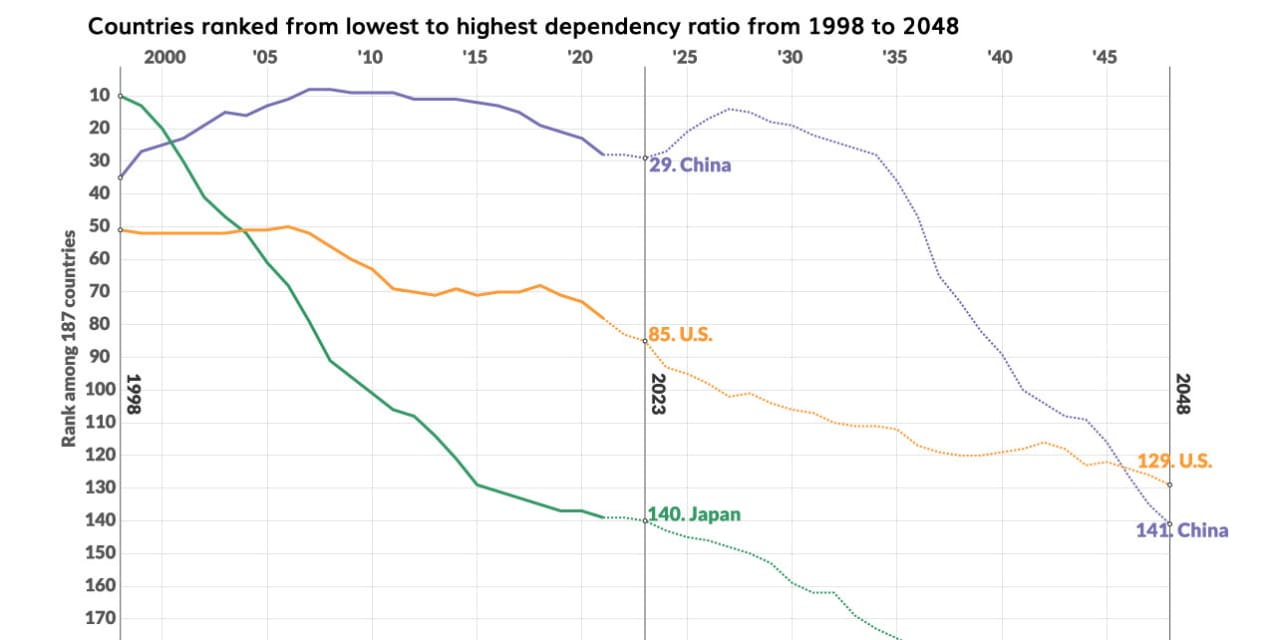
The dependency ratio is rising within the three largest economies by GDP.
The dependency ratio is calculated by defining which ages make up the working inhabitants and evaluating this complete with the remaining inhabitants (youth and aged) who don’t work. It’s used to find out the demographic dividend — the financial progress potential of a inhabitants. The decrease the ratio (i.e. 50 dependents for each 100 staff vs. 95 dependents for each 100 staff) the less non-workers a rustic must help.
This metric can be utilized to tell public coverage selections. So can the ideas associated to it, like who can work and the way a lot a working inhabitants can help a rustic’s dependents via taxes and reallocation of its nationwide funds.
Twenty 5 years in the past, in 1998, the dependency ratio of the U.S., primarily based on United Nations definitions, was 0.55, or 55 dependents for each 100 staff. The ratio continued to fall to as little as 52 dependents per 100 staff in 2011. As child boomers started to retire extra quickly, nevertheless, the ratio started rising and it’s projected to maintain climbing for the following decade till retirements decelerate and the inhabitants continues to age. In 2048, 25 years sooner or later, the U.S. dependency ratio is projected to hit 67 dependents for each 100 staff.
The same however extra dramatic reversal has occurred in China. From 1998 to 2011, China’s dependency ratio fell from 52 dependents for each 100 staff to 40 dependents per 100 staff. But the low delivery charge from China’s one-child coverage, which led to 2015, now means there are at the moment fewer individuals coming into the workforce to exchange retirees. In 2048, the dependency ratio in China is predicted to achieve 70 dependents for each 100 staff.
Japan’s demographic problem, after all, is on an entire different degree. Its dependency ratio started its journey upward in 1993 from 46 dependents for 100 staff to 73 dependents per 100 staff in 2023. The life expectancy in Japan is the best of any nation and the fertility charge is 1.3 births for each girl, in accordance with the World Bank. These elements will push the dependency ratio as excessive as 96 dependents for each 100 staff 25 years from now, an nearly 1-to-1 break up between its working age and dependents.
Read: Retiring in Japan: Seniors significantly outnumber youthful staff — and that’s a giant downside for everybody
The dependency ratio just isn’t solely an vital issue for Wall Street and buyers. It’s an vital software that may assist direct all kinds of public coverage selections impacting an economic system.
On a world scale, the indicator is used to mark the place a rustic is when it comes to its demographic transition, or modifications in its age construction. One vital stage of transition happens when fertility charges lower and the working-aged inhabitants grows. Two Harvard economists, David E. Bloom and David Canning, coined the potential financial progress ensuing from this era of transition because the “demographic dividend.”
Qingfing Li is a statistician at Johns Hopkins University who develops fashions to current to determination makers of nations in sub-Saharan Africa and southeast Asia. Many nations in these two areas are coming into their demographic-dividend stage and may develop economically if sure coverage modifications are made. A paper co-authored by Li outlines these areas of policy-specific change, like bettering the standard of training, selling a tradition of financial savings via coverage and bettering healthcare.
Li talked to MarketWatch particularly about his work in Uganda, specializing in a mannequin that measures the impression of a publicly funded healthcare program. Right now, most healthcare prices in Uganda are paid out of pocket, however having a social insurance coverage program might enhance the well being of the inhabitants primarily based on proof from different nations. His mannequin might help coverage makers higher perceive the ins-and-outs of what a social coverage program might appear like.
“The country is actually making a cost effective investment if they invest in policies and education to capitalize on the demographic dividend, ” Li emphasised.
On a nationwide degree within the United States, the connection between labor and dependents impacts the composition of the federal funds, particularly in terms of spending on Social Security.
The Congressional Budget Office launched its newest outlook for Social Security spending and income in December. It confirmed that the fast improve in retirees from the baby-boom era within the subsequent decade, coupled with a rise in life expectancy because the century rolls on, will end in spending for this system exceeding income set on the present proportion of GDP.
According to Louise Sheiner, an economist fellow on the Brookings Institute suppose tank who researches the impact coverage modifications have on Social Security, there will probably be a fast rise within the dependency ratio that comes from the retirement of the newborn growth era. It will degree off as individuals stay longer, Sheiner added. As a outcome, a key coverage challenge stemming from this transformation within the dependency ratio will probably be whether or not or to not elevate the retirement age from 65 to 70.
Read: Opinion: We ought to battle inflation by adopting supply-side labor reforms that will encourage work
But Sheiner warns there are limits in utilizing the metric for most of these selections. While wealthier individuals are residing longer, these on the backside of the revenue distribution should not. Sheiner stated it’s vital to take such information into consideration when making selections that will take away advantages from those that want it.
“The increase in life expectancy that we’ve seen has been really uneven,” Sheiner stated. “People at the top of the income distribution have seen large increases in life expectancy, but people at the bottom have not.”
Another answer for a declining workforce is to vary U.S. immigration coverage, as U.C. Davis economist Giovanni Peri factors out.
While Peri can’t say what the outcomes of a selected coverage can be, his analysis reveals the consequences of doing nothing. He mentions Japan and China as two nations the place productiveness has dropped and no new immigration coverage has been launched to stem the tide.
Read: The answer to building’s labor scarcity? Women and immigrants, says Harvard researcher
He famous that the almost definitely immigration-policy response within the U.S. can be to increase the H1-B visa program, which might enable immigrants who’ve a school diploma to enter the workforce with out making them residents. Amid the present political local weather, Peri thinks it’s extraordinarily unlikely that the U.S. will implement a coverage change that will see extra lower-educated immigrants allowed into the nation.
“I don’t think immigrants will come in to fill those jobs. Not because we wouldn’t need them, not because there is not demand, not because this would not be economically efficient, but because the policy does not exist,” Peri stated.
Read additionally: Is it time to take one other take a look at authorized immigration?
A Competitive Disadvantage
The U.S., China and Japan are seeing their dependency ratios soar, decreasing their dependency-ratio rating among the many world’s nations.
Source web site: www.marketwatch.com