The distinctive 40-year interval from 1980 to 2020 characterised by principally financial enlargement within the U.S. will probably get replaced by a extra common sample of boom-bust cycles and frequent recessions, in accordance with analysts at Deutsche Bank
DB,
One motive is that larger inflation over the approaching many years will restrict central banks’ room to maneuver in and out of doors the U.S., given the strain to not sacrifice financial development, the analysts wrote in a long-term asset return examine launched on Monday. Meanwhile, with debt-to-GDP ranges now at multidecade highs, there’s the query of whether or not U.S. deficits can proceed being utilized by the federal government to increase the enterprise cycle, contemplating that borrowing prices have gotten structurally larger.
Deutsche Bank’s take consists of one brilliant be aware — that frequent recessions are inclined to translate into stronger long-run development — and comes as traders and merchants have been debating if and when the U.S. may slip into what some describe as essentially the most anticipated downturn ever. The U.S. has fallen into six recessions since January 1980, 4 of which lasted simply two to eight months. As of this month, the world’s largest financial system has already met 4 of the so-called “triggers” that Deutsche Bank says are wanted over a 12-month interval throughout a extra extended run-up to a recession: Increasing inflation and an inverting yield curve, in addition to rising short-term charges and oil costs.
“All-in-all, we think the most likely future is one of more frequent recessions and more boom-bust cycles. Ultimately, the long expansions of the last 40 years are likely to prove rarer moving forward,” mentioned Jim Reid, head of worldwide economics and thematic analysis, strategist Henry Allen, and analyst Galina Pozdnyakova. “That may seem undesirable on the face of it, but history tells us that recessions aren’t necessarily bad for growth in the long term. Indeed, looking at our sample of G7 countries, it is the U.S. that has had the most frequent recessions, but has stronger economic growth than its peers.”
Artificial intelligence has the potential to render some industries and jobs out of date, and “move us away from the managed, zombie-type world of the last couple of decades,” they wrote. “Whether it’s because the golden macro era of 1980-2020 is behind us or whether it’s because AI will significantly disrupt the status quo, the most likely scenario is that the era of long business cycles is over.” While this doesn’t must be unfavourable for long-term financial efficiency, “it will clearly maintain macro volatility into a system that was used to long periods of low volatility prior to the pandemic.”
In the U.S., recessions have made up a disproportionate quantity of the ten%-plus selloffs traditionally seen within the S&P 500 index. The median and common drawdown in these recessions is -21% and -26%, with 1932 or the peak of the Great Depression producing the largest selloff on report, in accordance with Deutsche Bank.
Nonetheless, the U.S. has maintained persistently higher long-term fairness efficiency than its G7 friends given its extra business-friendly monetary system, in accordance with Deutsche Bank’s analysis. That is demonstrated within the knowledge on nominal and actual multiasset class returns going again greater than 200 years, the place potential, for quite a few developed- and emerging-market economies.
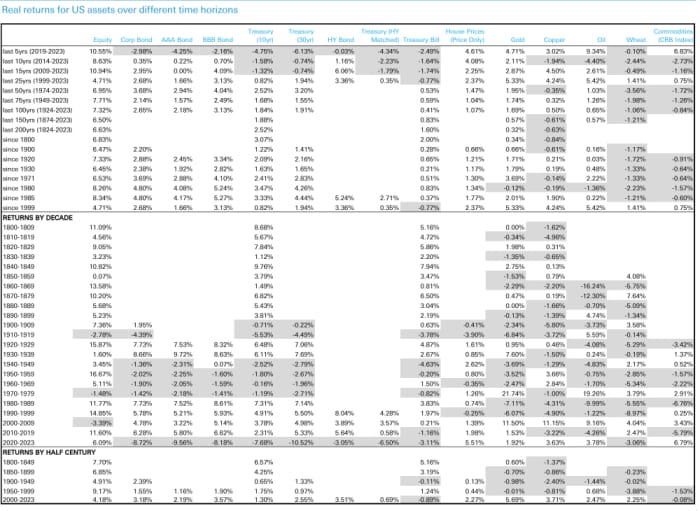
Source: Deutsche Bank, GFD, ICE Indices, Bloomberg LP. Any 2023 knowledge is as of Aug. 31. Shaded areas replicate unfavourable readings.
The Deutsche Bank group mentioned its purpose with the examine wasn’t to reply the query of whether or not the U.S. or Europe will fall right into a recession quickly. Rather, Reid, Allen and Pozdnyakova mentioned they wished to take a look at what historical past says concerning the frequency, depth, and length of recessions —together with what causes them.
Like the multiasset group at Rotterdam-based asset supervisor Robeco, Deutsche Bank takes a long-term view of occasions and steers clear of constructing any outright suggestions for traders.
Read: Here’s the ‘triple power play’ that will rule stock-market returns and different property for subsequent 5 years
Frankfurt-based Deutsche Bank, also known as Wall Street’s most pessimistic financial institution, was the primary big-name financial institution to name a U.S. recession in April 2022. The agency proved to be prescient in September of that yr when it noticed an nearly 5% fed-funds charge on the horizon, six months earlier than it got here to fruition.
As of Monday, all three main U.S. inventory indexes
SPX
DJIA
COMP
moved barely larger in New York afternoon buying and selling as traders sit up for the Federal Reserve’s coverage announcement in two days. Meanwhile, 2-
BX:TMUBMUSD02Y
by way of 10-year Treasury yields
BX:TMUBMUSD10Y
turned combined.
Read: Powell might nonetheless hammer U.S. shares on Wednesday even when the Fed doesn’t hike rates of interest
Source web site: www.marketwatch.com








